The Secrets To A Healthy Vegan Diet
Author: Dr. Stephen Chaney
 Osteoporosis is a debilitating and potentially deadly disease associated with aging. It affects 54 million Americans. It can cause debilitating back pain and bone fractures. 50% of women and 25% of men over 50 will break a bone due to osteoporosis. Hip fractures in the elderly due to osteoporosis are often a death sentence.
Osteoporosis is a debilitating and potentially deadly disease associated with aging. It affects 54 million Americans. It can cause debilitating back pain and bone fractures. 50% of women and 25% of men over 50 will break a bone due to osteoporosis. Hip fractures in the elderly due to osteoporosis are often a death sentence.
As I discussed in a previous issue of “Health Tips From The Professor”, a “bone-healthy lifestyle requires 3 essentials – calcium, vitamin D, and weight bearing exercise. If any of these three essentials is presence in inadequate amounts, you can’t build healthy bones. In addition, other nutrients such as protein, magnesium, zinc, vitamin B12, and omega-3 fatty acids may play supporting roles.
Vegan and other plant-based diets are thought to be very healthy. They decrease the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and some cancers. However, vegan diets tend to be low in calcium, vitamin D, zinc, vitamin B12, protein, and omega-3 fatty acids. Could vegan diets be bad for your bones?
A meta-analysis of 9 studies published in 2009 (LT Ho-Pham et al, American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 90: 943-950, 2009) reported that vegans had 4% lower bone density than omnivores, but concluded this difference was “not likely to be clinically relevant”.
However, that study did not actually compare bone fracture rates in vegans and omnivores. So, investigators have followed up with a much larger meta-analysis (I Iguacel et al, Nutrition Reviews 77, 1-18, 2019) comparing both bone density and bone fracture rates in vegans and omnivores.
How Was This Study Done?
 The investigators searched the literature for all human clinical studies through November 2017 that compared bone densities and frequency of bone fractures of people consuming vegan and/or vegetarian diets with people consuming an omnivore diet.
The investigators searched the literature for all human clinical studies through November 2017 that compared bone densities and frequency of bone fractures of people consuming vegan and/or vegetarian diets with people consuming an omnivore diet.
- Vegan diets were defined as excluding all animal foods.
- Vegetarian diets were defined as excluding meat, poultry, fish, seafood, and flesh from any animal but including dairy foods and/or eggs. [Note: The more common name for this kind of diet is lacto-ovo vegetarian, but I will use the author’s nomenclature in this review.]
- Omnivore diets were defined as including both plant and animal foods from every food group.
The investigators ended up with 20 studies that had a total of 37,134 participants. Of the 20 studies, 9 were conducted in Asia (Taiwan, Vietnam, India, Korea, and Hong-Kong), 6 in North America (the United States and Canada), and 4 were conducted in Europe (Italy, Finland, Slovakia, and the United Kingdom).
Are Vegan Diets Bad For Your Bones?
Here is what the investigators found:
 Bone density: The clinical studies included 3 different sites for bone density measurements – the lumbar spine, the femoral neck, and the total body. When they compared bone density of vegans and vegetarians with the bone density of omnivores, here is what they found:
Bone density: The clinical studies included 3 different sites for bone density measurements – the lumbar spine, the femoral neck, and the total body. When they compared bone density of vegans and vegetarians with the bone density of omnivores, here is what they found:
Lumbar spine:
-
- Vegans and vegetarians combined had a 3.2% lower bone density than omnivores.
-
- The effect of diet was stronger for vegans (7% decrease in bone density) than it was for vegetarians (2.3% decrease in bone density).
Femoral neck:
-
- Vegans and vegetarians combined had a 3.7% lower bone density than omnivores.
-
- The effect of diet was stronger for vegans (5.5% decrease in bone density) than it was for vegetarians (2.5% decrease in bone density).
Whole body:
-
- Vegans and vegetarians combined had a 3.2% lower bone density than omnivores.
-
- The effect of diet was statistically significant for vegans (5.9% decrease in bone density) but not for vegetarians (3.5% decrease in bone density). [Note: Statistical significance is not determined by how much bone density is decreased. It is determined by the size of the sample and the variations in bone density among individuals in the sample.]
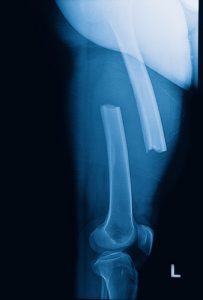 Bone Fractures: The decrease in bone density of vegans in this study was similar to that reported in the 2009 study I discussed above. However, rather than simply speculating about the clinical significance of this decrease in bone density, the authors of this study also measured the frequency of fractures in vegans, vegetarians, and omnivores. Here is what they found.
Bone Fractures: The decrease in bone density of vegans in this study was similar to that reported in the 2009 study I discussed above. However, rather than simply speculating about the clinical significance of this decrease in bone density, the authors of this study also measured the frequency of fractures in vegans, vegetarians, and omnivores. Here is what they found.
- Vegans and vegetarians combined had a 32% higher risk of bone fractures than omnivores.
- The effect of diet on risk of bone fractures was statistically significant for vegans (44% higher risk of bone fracture) but not for vegetarians (25% higher risk of bone fractures).
- These data suggest the decreased bone density in vegans is clinically significant.
The authors concluded, “The findings of this study suggest that both vegetarian and vegan diets are associated with lower bone density compared with omnivorous diets. The effect of vegan diets on bone density is more pronounced than the effect of vegetarian diets, and vegans have a higher fracture risk than omnivores. Both vegetarian and vegan diets should be appropriate planned to avoid dietary deficiencies associated with bone health.”
The Secrets To A Healthy Vegan Diet
![]() The answer to this question lies in the last statement in the author’s conclusion, “Both vegetarian and vegan diets should be appropriate planned to avoid dietary deficiencies associated with bone health.”
The answer to this question lies in the last statement in the author’s conclusion, “Both vegetarian and vegan diets should be appropriate planned to avoid dietary deficiencies associated with bone health.”
The problem also lies in the difference between what a nutrition expert considers a vegan diet and what the average consumer considers a vegan diet. To the average consumer a vegan diet is simply a diet without any animal foods. What could go wrong with that definition? Let me count the ways.
- Sugar and white flour are vegan. A vegan expert thinks of a vegan diet as a whole food diet – primarily fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, nuts, and seeds. A vegan novice includes all their favorites – sodas, sweets, and highly processed foods. And that may not leave much room for healthier vegan foods.
2) Big Food, Inc is not your friend. Big Food tells you that you don’t need to give up the taste of animal foods just because you are going vegan. They will just combine sugar, white flour, and a witch’s brew of chemicals to give you foods that taste just like your favorite meats and dairy foods. The problem is these are all highly processed foods. They are not healthy. Some people call them “fake meats” or “fake cheeses”. I call them “fake vegan”.
If you are going vegan, embrace your new diet. Bean burgers may not taste like Big Macs, but they are delicious. If need other delicious vegan recipe ideas, I recommend the website https://forksoverknives.com.
3) A bone healthy vegan diet is possible, but it’s not easy. Let’s go back to the author’s phrase “…vegan diets should be appropriate planned to avoid dietary deficiencies associated with bone health.” A vegan expert will do the necessary planning. A vegan novice will assume all they need to do is give up animal foods.
As I said earlier, vegan diets tend to be low in calcium, vitamin D, zinc, vitamin B12, protein, and omega-3 fatty acids. Let’s look at how a vegan expert might plan their diet to get enough of those bone-healthy nutrients.
-
- Calcium. The top plant sources of calcium are leafy greens and soy foods at about 100-250 mg (10-25% of the DV) of calcium per serving. Some beans and seeds are moderately good sources of calcium. Soy foods are a particularly good choice because they are a good source of calcium and contain phytoestrogens that stimulate bone formation.
A vegan expert makes sure they get these foods every day and often adds a calcium supplement.
It drives me crazy when a vegan novice tells me they were told they can get all the protein they need from broccoli and leafy greens. That is incredibly bad advice.
A vegan expert makes sure they get soy foods, beans, and protein-rich grains every day and often adds a protein supplement.
-
- Zinc. There are several plant foods that supply around 20% the DV for zinc including lentils, oatmeal, wild rice, squash and pumpkin seeds, quinoa, and black beans.
A vegan expert makes sure they get these foods every day and often adds a multivitamin supplement containing zinc.
-
- Vitamin D and vitamin B12. These are very difficult to get from a vegan diet. Even vegan experts usually rely on supplements to get enough of these important nutrients.
4) Certain vegan foods can even be bad for your bones. I divide these into healthy vegan foods and unhealthy “vegan” foods.
-
- Healthy vegan foods that can be bad for your bones include.
-
-
- Pinto beans, navy beans, and peas because they contain phytates.
-
-
-
- Raw spinach & swiss chard because they contain oxalates.
-
-
-
- Both phytates and oxalates bind calcium and interfere with its absorption.
-
-
-
- These foods can be part of a healthy vegan diet, but a vegan expert consumes them in moderation.
-
-
- Unhealthy “vegan” foods that are bad for your bones include sodas, salt, sugar, and alcohol.
-
-
- The mechanisms are complex, but these foods all tend to dissolve bone.
-
-
-
- A vegan expert minimizes them in their diet.
-
5) You need more than diet for healthy bones. At the beginning of this article, I talked about the 3  essentials for bone formation – calcium, vitamin D, and exercise. You can have the healthiest vegan diet in the world, but if you aren’t getting enough weight bearing exercise, you will have low bone density. Let me close with 3 quick thoughts:
essentials for bone formation – calcium, vitamin D, and exercise. You can have the healthiest vegan diet in the world, but if you aren’t getting enough weight bearing exercise, you will have low bone density. Let me close with 3 quick thoughts:
-
- None of the studies included in this meta-analysis measured how much exercise the study participants were getting.
-
- The individual studies were generally carried out in industrialized countries where many people get insufficient exercise.
-
- The DV for calcium in the United States is 1,000-1,200 mg/day for adults. In more agrarian societies dietary calcium intake is around 500 mg/day, and osteoporosis is almost nonexistent. What is the difference? These are people who are outside (vitamin D) doing heavy manual labor (exercise) in their farms and pastures every day.
In summary, a bone healthy vegan lifestyle isn’t easy, but it is possible if you work at it.
The Bottom Line
A recent meta-analysis asked two important questions about vegan diets.
- Do vegans have lower bone density than omnivores?
2) Is the difference in bone density clinically significant? Are vegans more likely to suffer from bone fractures?
The study found that:
- Vegans had 5.5%–7% lower bone density than omnivores depending on where the bone density was measured.
- Vegans were 44% more likely to suffer from bone fractures than omnivores.
The authors of the study concluded, ““The findings of this study suggest that…vegan diets are associated with lower bone density compared with omnivorous diets, and vegans have a higher fracture risk than omnivores…Vegan diets should be appropriate planned to avoid dietary deficiencies associated with bone health.”
In evaluating the results of this study, I took a detailed look at the pros and cons of vegan diets and concluded, “A bone healthy vegan lifestyle isn’t easy, but it is possible if you work at it.”
For more details about study and my recommendations for a bone healthy vegan lifestyle read the article above.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.