How Do Omega-3s Affect The Two Types Of Stroke?
Author: Dr. Stephen Chaney
 I am continuing my series on recent omega-3 breakthroughs. Last week I reviewed a study showing that the omega-3s EPA and DHA lowered blood pressure. Since high blood pressure is a major contributing factor to stroke risk, it only makes sense that EPA and DHA would also decrease the risk of strokes.
I am continuing my series on recent omega-3 breakthroughs. Last week I reviewed a study showing that the omega-3s EPA and DHA lowered blood pressure. Since high blood pressure is a major contributing factor to stroke risk, it only makes sense that EPA and DHA would also decrease the risk of strokes.
In last week’s article I mentioned that high blood pressure is called a silent killer. That is because the symptoms of high blood pressure are easy to ignore and often confused with other illnesses.
For many people the first indication they have a problem is when they have a stroke, which either kills them or forever impacts their quality of life. Let me share some statistics with you.
- Every 40 seconds someone in the United States has a stroke. One in four adults over the age of 25 will have a stroke in their lifetime.
- Every 4 minutes someone in the United States dies from a stroke. For many of them sudden death is the first indication they had a health problem.
- The overall incidence of strokes has increased 60% in the last 20 years with most of that increase (65%) coming from younger adults (ages 20 to 45)
- The cost of treatment, rehabilitation, and lost wages from stroke was $891 billion in 2020 and is projected to increase to $2.3 trillion in 2050.
Any way you look at it, the personal and financial costs of strokes are immense.
How Do Omega-3s Affect The Two Types Of Stroke?
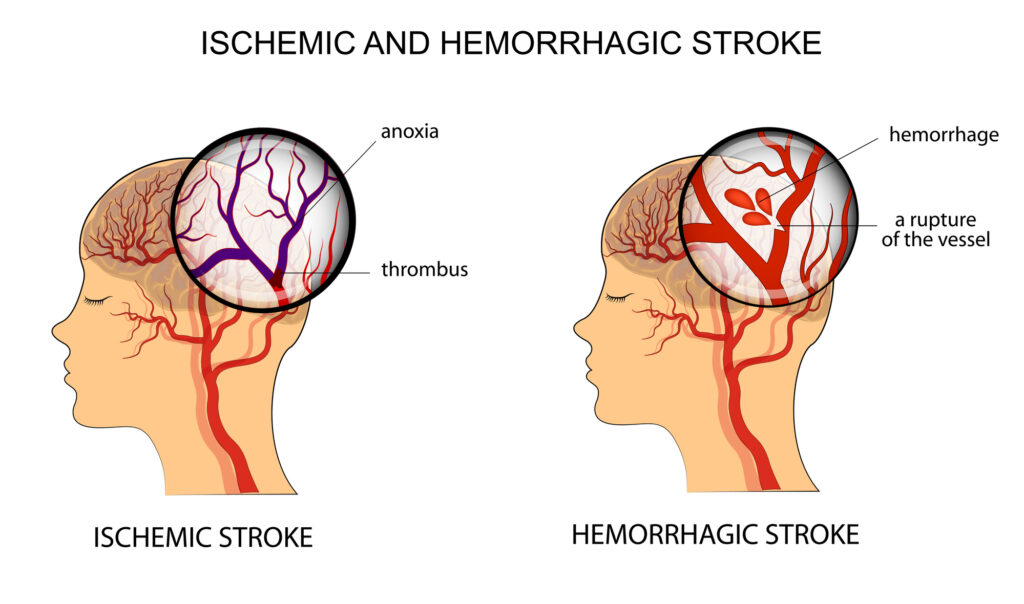 There are two major kinds of stroke – ischemic stroke, which is caused by a thrombus (blood clot) in the carotid arteries leading to the brain, and hemorrhagic stroke, which is caused by bleeding from small blood vessels in the brain. Ischemic stroke accounts for around 85% of all strokes.
There are two major kinds of stroke – ischemic stroke, which is caused by a thrombus (blood clot) in the carotid arteries leading to the brain, and hemorrhagic stroke, which is caused by bleeding from small blood vessels in the brain. Ischemic stroke accounts for around 85% of all strokes.
Ischemic strokes are caused by atherosclerosis, the buildup of fatty plaques in the walls of the carotid arteries, followed by the formation of a blood clot which lodges in the narrowed arteries. As you might expect, the prevention and treatment of ischemic strokes are similar to the prevention and treatment of heart attacks.
EPA and DHA have been shown to:
- Reduce inflammation, which is associated with increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Reduce blood pressure. High blood pressure damages the endothelial lining of blood vessels, which can lead to either build up of atherosclerotic plaque or rupturing of the blood vessels.
- Reduce platelet aggregation and blood viscosity, which reduces the potential for inappropriate blood clots forming in the carotid arteries.
[When you cut yourself, you want a blood clot to form to stop the bleeding. That is an example of appropriate blood clot formation. However, when a blood clot forms within your arteries, it can prevent blood from reaching surrounding tissues. This is an example of inappropriate blood clot formation.]
- Reduce the risk of atherosclerotic plaques rupturing. Rupturing of atherosclerotic plaques triggers blood clot formation, so this also decreases the risk of inappropriate blood clots forming in the carotid arteries.
Based on the known effects of EPA and DHA, it is not surprising that they would decrease the risk of ischemic strokes. But what about hemorrhagic strokes? Here the answer is not as clear cut.
- In a previous clinical study 4 gm/day of purified EPA without DHA was associated with a slightly increased risk of bleeding events but did not increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
- High doses of pharmaceutical grade EPA have also been associated with a slightly increased risk of atrial fibrillation (Afib). In contrast, previous studies have shown that higher dietary intake of EPA + DHA are associated with a lower risk of Afib.
At present, we don’t know whether the increased risk of bleeding events and Afib are only seen at very high doses of omega-3s or are due to the use of pharmaceutical grade EPA without DHA and any of the other naturally occurring omega-3s.
However, this uncertainty has led some experts to warn that omega-3s may be a two-edge sword. They might increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke while decreasing the risk of ischemic stroke. This uncertainty was part of the rationale for the study (JH O’Keefe et al, Stroke, 55: 50-58, 2024) I am describing today.
How Was This Study Done?
 This study was a meta-analysis of 29 clinical studies looking at the effect of omega-3 fatty acids on the risk of both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. These studies were performed in 15 countries from around the world and included a total of 183,291 participants.
This study was a meta-analysis of 29 clinical studies looking at the effect of omega-3 fatty acids on the risk of both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. These studies were performed in 15 countries from around the world and included a total of 183,291 participants.
One major drawback of many meta-analyses is that each study in the meta-analysis is independently designed. Sometimes the studies are so different that it is difficult to fit them together in a coherent pattern.
A major strength of this meta-analysis is that all the studies were conducted within the “Fatty Acid and Outcome Research Consortium” which specifies a general protocol for the design of each study within that consortium.
For example, estimates of dietary omega-3 intake can be inaccurate and the uptake and utilization of both dietary and supplemental omega-3s vary from person to person. Because of that the Fatty Acid and Outcomes Research Consortium guideline specifies that studies rely on biomarkers of omega-3 levels in the body rather than the amount of omega-3s consumed.
The most frequently used biomarker was the percentage of omega-3s incorporated into the fatty portion of red blood cell membranes. Some studies used other biomarkers, such as the percentage of omega-3s incorporated into the fatty portion of plasma phospholipids or cholesterol-containing phospholipid particles (LDL and HDL for example).
In each case, the percentage of omega-3s is used to calculate something called an “Omega-3 Index”. Previous studies have shown that an Omega-3 Index of 4% or less correlates with a high risk of heart disease, and an Omega-3 Index of 8% or more correlates with a low risk of heart disease. In essence, this study correlated Omega-3 Index with the risk of stroke.
The Fatty Acids and Outcomes Research Consortium harmonized the studies included in this meta-analysis in several other ways, but the use of Omega-3 Index rather than omega-3 consumption was the most important.
Other key characteristics of the studies included in this meta-anaysis were:
- The average age of participants was 65 years.
- 82% of the participants were white and 53% were women.
- The average length of follow-up was 14 years (range = 5-30 years).
- 10,561 participants (5.8%) suffered a stroke during follow-up (78% ischemic, 11% hemorrhagic, and 11% unspecified).
The Good News About Omega-3s and Stroke
 The participants in these studies were divided into quintiles based on their Omega-3 Index. When those in the highest quintile (≥ 8%) were compared with those in the lowest quintile (≤ 4%):
The participants in these studies were divided into quintiles based on their Omega-3 Index. When those in the highest quintile (≥ 8%) were compared with those in the lowest quintile (≤ 4%):
- Risk was reduced by 17% for total stroke and 18% for ischemic stroke. There was no effect on hemorrhagic stroke.
When the effect of individual components of the Omega-3 Index were analyzed:
- For EPA + DHA risk was reduced by 17% for total stroke and 18% for ischemic stroke. There was no effect on hemorrhagic stroke.
- For EPA risk was reduced by 17% for total stroke and 18% for ischemic stroke. There was no effect on hemorrhagic stroke. (You are probably starting to detect a pattern).
- For DHA the results were only slightly different. Risk reduction was 12% for total stroke and 16% for ischemic stroke. There was no effect on hemorrhagic stroke.
- For DPA, a minor component of the Omega-3 Index, there was no significant effect on total, ischemic, or hemorrhagic stroke.
- There was a linear dose-response for the effect of EPA, DHA, and the two combined on the reduction in risk for both total and ischemic stroke.
When they looked at subgroups within the analysis, the results were the same for:
- Age (<65 compared to >65).
- Gender.
- Studies that lasted less than 10 years and studies that lasted more than 10 years.
- The presence of preexisting Afib.
- The presence of preexisting cardiovascular disease.
The authors concluded, “In summary, this harmonized and pooled analysis of prospective studies showed that long-chain omega-3 levels were inversely associated with risk of total and ischemic stroke but were unrelated to risk of hemorrhagic stroke. Thus, higher dietary intake of DHA and EPA would be expected to lower risk of stroke.”
What Does This Study Mean For You?
 Key Takeaways From This Study: The most important takeaway from this study is that reasonable amounts of EPA and DHA from either diet or supplementation are unlikely to increase your risk of hemorrhagic stroke (I will define reasonable below).
Key Takeaways From This Study: The most important takeaway from this study is that reasonable amounts of EPA and DHA from either diet or supplementation are unlikely to increase your risk of hemorrhagic stroke (I will define reasonable below).
That is important to know because this and several other studies show that EPA and DHA decrease the risk of ischemic stroke, which accounts for around 85% of total strokes. This study shows you can reduce your risk of ischemic stroke without fearing that you will increase your risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
This study also reaffirms the importance of relying on Omega-3 Index rather than the dosage of omega-3s in a supplementation. Previous studies have shown there is significant individual variability in the uptake and utilization of dietary omega-3s.
Finally, this study shows you don’t need huge amounts of EPA and DHA to significantly decrease your risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease in general. An Omega-3 Index of ≥ 8% is sufficient to accomplish both.
How Much Omega-3s Do You Need? The authors of this manuscript are experts on the Omega-3 Index, and they estimated that:
- To raise your Omega-3 Index from 5.4% (the median Omega-3 Index in these studies) to 8% would require about 1,000 mg/d of EPA + DHA.
- To raise your Omega-3 Index from 3.5% (the lowest Omega-3 Index quintile in these studies) to 8% would require about 1,600 mg/d of EPA + DHA.
These intakes are well within the American Heart Association recommendations for reducing the risk of stroke and cardiovascular disease and are easily achievable from diet and supplementation.
But these estimates are based on averages, and, as I noted above, none of us are average. We differ in our ability to absorb and utilize omega-3s. So, I recommend relying on your Omega-3 Index rather than a dose of omega-3s that’s right for the average person but may not be right for you.
My recommendation would be to start with an Omega-3 test. If you are below 8%, start with the dosage of EPA + DHA the authors of today’s study recommended. Then retest in 6 months and adjust your dose based on the results of that test.
 How Much Is Too Much? As I mentioned above, the dose response was linear for Omega-3 Index versus reduction in risk of total and ischemic strokes. So, the question becomes whether you might wish to increase your Omega-3 Index above 8% to achieve an even better reduction in stroke risk.
How Much Is Too Much? As I mentioned above, the dose response was linear for Omega-3 Index versus reduction in risk of total and ischemic strokes. So, the question becomes whether you might wish to increase your Omega-3 Index above 8% to achieve an even better reduction in stroke risk.
That is a very personal decision that only you can make but let me share some facts to help you make that decision.
- As I mentioned above, a previous clinical trial showed an increased risk of bleeding events and Afib at a dosage of 4 gm/day of pure EPA. We don’t know whether that was because of the dose or the use of a formulation that contained only EPA without DHA and other naturally occurring long-chain omega-3s.
- In that study the increase in bleeding events and Afib was observed in <5% of participants, which suggests that those side effects may be limited to certain high-risk individuals.
-
- In this context, high risk might include individuals with preexisting Afib, individuals with a tendency towards excess bleeding, and patients on blood thinning medications.
-
- However, only your physician knows all your risk factors. If you have health issues or are on medications, it is always a good idea to check with your physician before changing your omega-3 intake. And if you are considering high-dose omega-3 supplementation or exceeding an 8% Omega-3 Index, I strongly recommend that you consult with your physician first.
The Bottom Line
A recent study looked at the effect of omega-3 levels in red blood cells and other tissues (something called Omega-3 Index) on the risk of various types of stroke.
When individuals with an Omega-3 Index ≥ 8% were compared with those with an Omega-3 Index of ≤ 4%:
- Risk was reduced by 17% for total stroke and 18% for ischemic stroke (stroke caused by blood clots in the carotid arteries). There was no effect on hemorrhagic stroke (stroke caused by bleeding from small blood vessels in the brain).
The authors concluded, “In summary, this harmonized and pooled analysis of prospective studies showed that long-chain omega-3 levels were inversely associated with risk of total and ischemic stroke but were unrelated to risk of hemorrhagic stroke. Thus, higher dietary intake of DHA and EPA would be expected to lower risk of stroke.”
This study represents an important breakthrough. There is good evidence that increased EPA + DHA from food and/or supplements reduces the risk of ischemic stroke. But some experts have cautioned it might also increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. This study puts that fear to rest.
For more details about the study and what it means for you, read the article above.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
_______________________________________________________________________________
My posts and “Health Tips From the Professor” articles carefully avoid claims about any brand of supplement or manufacturer of supplements. However, I am often asked by representatives of supplement companies if they can share them with their customers.
My answer is, “Yes, as long as you share only the article without any additions or alterations. In particular, you should avoid adding any mention of your company or your company’s products. If you were to do that, you could be making what the FTC and FDA consider a “misleading health claim” that could result in legal action against you and the company you represent.
For more detail about FTC regulations for health claims, see this link.
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/health-products-compliance-guidance
About The Author
 Dr. Chaney has a BS in Chemistry from Duke University and a PhD in Biochemistry from UCLA. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of North Carolina where he taught biochemistry and nutrition to medical and dental students for 40 years. Dr. Chaney won numerous teaching awards at UNC, including the Academy of Educators “Excellence in Teaching Lifetime Achievement Award”. Dr Chaney also ran an active cancer research program at UNC and published over 100 scientific articles and reviews in peer-reviewed scientific journals. In addition, he authored two chapters on nutrition in one of the leading biochemistry text books for medical students.
Dr. Chaney has a BS in Chemistry from Duke University and a PhD in Biochemistry from UCLA. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of North Carolina where he taught biochemistry and nutrition to medical and dental students for 40 years. Dr. Chaney won numerous teaching awards at UNC, including the Academy of Educators “Excellence in Teaching Lifetime Achievement Award”. Dr Chaney also ran an active cancer research program at UNC and published over 100 scientific articles and reviews in peer-reviewed scientific journals. In addition, he authored two chapters on nutrition in one of the leading biochemistry text books for medical students.
Since retiring from the University of North Carolina, he has been writing a weekly health blog called “Health Tips From the Professor”. He has also written two best-selling books, “Slaying the Food Myths” and “Slaying the Supplement Myths”. And most recently he has created an online lifestyle change course, “Create Your Personal Health Zone”. For more information visit https://chaneyhealth.com.
For the past 45 years Dr. Chaney and his wife Suzanne have been helping people improve their health holistically through a combination of good diet, exercise, weight control and appropriate supplementation.