The Role Of Muscle Protein In Energy Metabolism
Author: Dr. Stephen Chaney
 We’ve been told, It’s all downhill after 30.” That may or may not be true depending on the lifestyle choices we make.
We’ve been told, It’s all downhill after 30.” That may or may not be true depending on the lifestyle choices we make.
But for muscle mass, “It’s all downhill after 50!” Simply put, we start to lose muscle mass at an accelerating pace after 50, a process scientists call sarcopenia.
Sarcopenia should be a major concern for everyone over 50. Loss of muscle mass:
- Causes unsteadiness which can lead to falls, bone fractures, and death.
- Increases the risk of obesity because muscle burns more calories than fat. That increases our risk of obesity-related diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, some cancers, osteoarthritis, and other inflammatory diseases.
- Robs us of the fun activities we would like to enjoy in our golden years.
But sarcopenia is not inevitable. As I have discussed in previous issues of “Health Tips From the Professor”, there are three things we can do to minimize sarcopenia as we age.
- Get adequate weight-bearing exercise. In other words, pump iron or use your body weight.
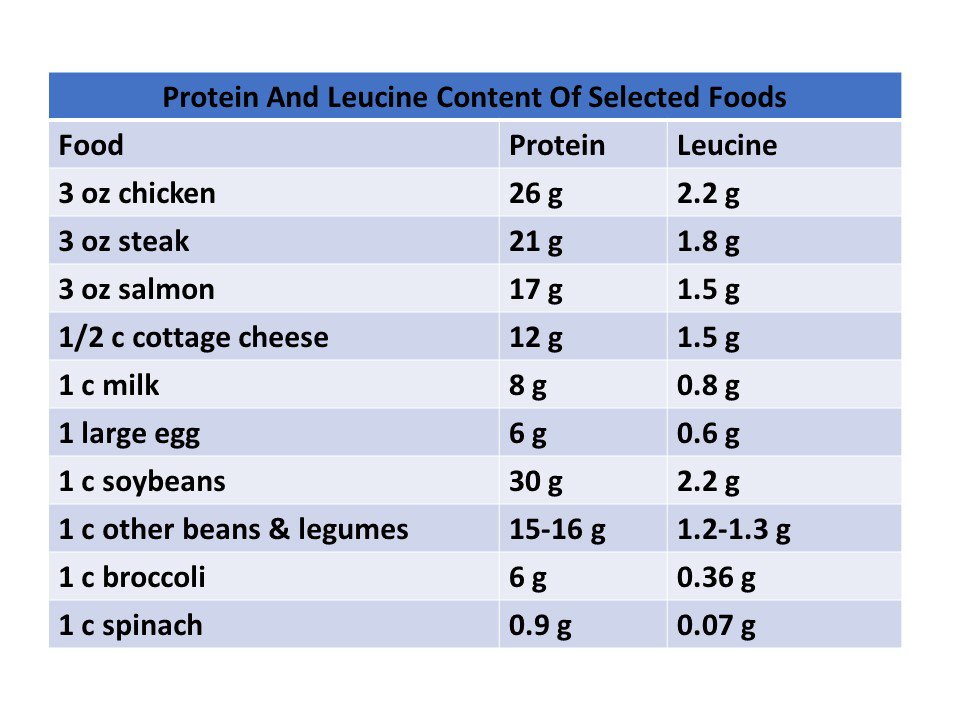
- Get adequate amounts of the branched-chain amino acid leucine.
In this article I will focus on the last two, especially the fact that we need more protein and leucine to prevent loss of muscle mass as we age. To help you understand why that is, I am going to share my favorite topic – Metabolism 101 (Once a biochemistry professor, always a biochemistry professor).
Metabolism 101: The Role Of Muscle Protein In Energy Metabolism
 Most people associate muscle mass with strength and endurance. Many understand the important role muscle mass plays in burning off excess calories and keeping us slim. But few people understand the important role that muscle protein plays in our everyday energy metabolism.
Most people associate muscle mass with strength and endurance. Many understand the important role muscle mass plays in burning off excess calories and keeping us slim. But few people understand the important role that muscle protein plays in our everyday energy metabolism.
Let’s start with an overview of metabolism [Note: If you are not interested in this, you can just skip over the bullets and read the take-home message at the bottom of this section.]
- We get energy from the carbohydrate, fat, and protein we consume. Excess carbohydrate, fat, and protein in our meals are stored to provide the energy our body needs between meals and during prolonged fasting.
-
- We have a virtually unlimited ability to store fat, as some of you may have noticed.
-
- We have a very limited ability to store carbohydrates in the form of glycogen in our liver.
-
- Our ability to store protein is even more limited, even when protein intake is coupled with exercise. And muscle protein plays other very important functions. It is a precious resource.
-
- Finally, any carbohydrate and protein beyond our body’s ability to store it is converted to and stored as fat.
- In the fed state most of our energy is derived from blood glucose. This is primarily controlled by the hormone insulin. As blood glucose levels fall, we move to the fasting state and start to call on our stored energy sources to keep our body functioning. This process is primarily controlled by a hormone called glucagon.
-
- In the fasting state most tissues easily switch to using fat as their main energy source, but…
-
-
- Red blood cells and a few other tissues in the body are totally dependent on glucose as an energy source.
-
-
- Initially our brain is totally dependent on glucose as an energy source, and our brains use a lot of energy. [Note: Our brain can switch to ketones as an energy source with prolonged starvation or prolonged carbohydrate restriction, but that’s another story for another day.]
- Because our brain and other tissues need glucose in the fasting state, it is important to maintain a constant blood glucose level between meals.
-
- Initially, blood glucose levels are maintained by calling on the glycogen reserves in the liver.
-
- But because these reserves are limited, our body starts to break down muscle protein and convert it to glucose as well – even in the normal dinner/sleep/breakfast cycle.
You may have found the explanation above was excessive, but I couldn’t think of a simpler way of helping you understand that in addition to its other important role in the body, muscle protein is also an energy store.
When we eat, we make a deposit to that energy store. Between meals we withdraw from that energy store. When we are young the system works perfectly. Unless we fast for prolonged periods of time, we are always adding enough muscle protein in the fed state to balance out the withdrawals between meals.
But as we age, our ability to build muscle in the fed state becomes less efficient. Withdrawals exceed deposits, and we experience age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia).
What We Know About Preventing Age-Related Muscle Loss
 As I said above, there are three things needed to prevent age-related muscle loss:
As I said above, there are three things needed to prevent age-related muscle loss:
- Adequate resistance exercise.
- Adequate amounts of protein.
- Adequate amounts of the essential, branched-chain amino acid called leucine.
And, as I said above, I am going to focus on the last two.
In previous issues of “Health Tips From the Professor” I have shared articles showing that the amount of both protein and leucine needed to maximize the gain in muscle mass following a meal or a workout increase as we age. For example:
- For someone in their 30s, 15-20 grams of protein with 1.7 grams of leucine per meal is optimal.
- But someone in their 60’s and 70s needs 25-30 grams of protein and 2.5-2.7 grams of leucine per meal to achieve the same effect.
- Most of these studies have been done with men, but a recent study showed the results are identical with post-menopausal women.
However, previous studies have not addressed the role of protein supplementation in achieving adequate protein intake or what kind of protein supplements were best. The studies I will discuss today were designed to answer these questions.
How Were These Studies Done?
 Study #1: As I said above, previous studies have suggested that 25-30 grams of protein per meal is optimal for preventing age-related loss of muscle mass in seniors. However, many seniors get most of their protein in their evening meal. On average, seniors consume 8-15 grams of protein at breakfast, 15-20 grams of protein at lunch, and 30-40 grams of protein at dinner.
Study #1: As I said above, previous studies have suggested that 25-30 grams of protein per meal is optimal for preventing age-related loss of muscle mass in seniors. However, many seniors get most of their protein in their evening meal. On average, seniors consume 8-15 grams of protein at breakfast, 15-20 grams of protein at lunch, and 30-40 grams of protein at dinner.
This study (C Norton et al, The Journal of Nutrition, 146: 65-67, 2016) was designed to ask whether optimizing protein intake at each meal by adding a protein supplement at breakfast and lunch would increase lean muscle mass in seniors over a 24 week period.
The investigators recruited 60 adults, aged 50-70 (average age = 61) from the city of Limerick, Ireland. The participants were 73% women and had an average BMI of 25.8 (slightly overweight).
The participants were randomly assigned to receive either a milk-based supplement or an isocaloric, non-protein containing, maltrodextrin control. The protein supplement provided 15 grams of protein. The participants were instructed not to change any other aspect of their diet or activity level.
The protein supplement and placebo were provided in identical sachets and the participants were told to mix them with water and consume them with breakfast and lunch. The protein supplement and placebo looked and tasted identical, so the subjects did not know which group they were in. Compliance was assessed by collecting the used sachets at the end of the study.
The participants completed 4-day diet recalls under the supervision of a dietitian before and during the study. Lean muscle mass was determined prior to and at the end of the 24-week study.
 Study #2: This study (J McKendry et al, The American Journal Of Clinical Nutrition, doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2024.05.009) was designed to determine whether the ability to stimulate muscle protein synthesis depended on the type of supplemental protein.
Study #2: This study (J McKendry et al, The American Journal Of Clinical Nutrition, doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2024.05.009) was designed to determine whether the ability to stimulate muscle protein synthesis depended on the type of supplemental protein.
This study was built on the results of the first study. Specifically, the investigators compared the effect on muscle protein synthesis of adding 25 grams of whey, pea, or collagen protein to the breakfast and lunch meals.
The investigators enrolled 31 healthy, older (average age = 72) subjects from the Hamilton, Ontario area. Subjects were excluded from the study if:
- They had a medical condition or were taking any medication that might influence the results.
- They used tobacco or tobacco related products.
- They consumed a vegan or vegetarian diet
- They used a walking device or were inactive for any reason.
The participants were placed on a standardized diet consisting of prepackaged meals (breakfast, lunch, and dinner) and a mix of fruits, vegetables, snacks, and drinks. They were instructed to only eat the foods provided to them and to maintain their normal activity levels.
The diet was designed to provide the RDA for protein (0.8 gram of protein/kilogram of body weight) and to mimic the habitual dietary patterns of seniors in the United States and Canada.
- Around 55% carbohydrate, 30% fat, and 15% protein.
- Uneven distribution of protein through the day (19% at breakfast, 26% at lunch, and 55% at dinner).
After one week on the control diet, participants were randomly assigned to receive 25-gram protein supplements of either whey, pea, or collagen protein and instructed to add them to their standardized diet for breakfast and lunch (total protein intake was increased by 50 grams/day). They followed this regimen for 7 days.
On day one and 7 of the control phase and on day 7 of the intervention phase (when the participants were consuming additional protein) muscle biopsies were obtained 90 minutes after breakfast for determination of the effect of the meal on muscle protein synthesis.
[Note: The participants were consuming a protein supplement containing an additional 25 grams of protein at both breakfast and lunch. But the effect of this additional protein on protein synthesis was only determined after the breakfast meal.]
Optimizing Protein Content For Seniors
Each of the studies provided important insights for anyone wanting to minimize age-related muscle loss.
Study #1: The effect of the whey protein supplement for breakfast and lunch on protein intake was as follows:
| Protein Intake In Grams |
| Meal |
Baseline |
Plus Protein Supplement |
| Breakfast |
15 |
27 |
| Lunch |
22 |
34 |
| Dinner |
38 |
38 |
| Snacks |
8 |
7 |
| Total |
83 |
106 |
[Note: The amount of additional protein from diet and supplementation averaged around 12 grams/meal instead of 15 grams in the supplemental protein provided. The investigators did not address this, but I suspect the participants may have cut back on their regular food intake because the protein supplement reduced their appetite.]
The results were clear cut:
- Protein supplementation at breakfast and lunch resulted in a 1.3-pound gain in lean body mass over 24 weeks compared to the control group using an isocaloric, non-protein containing maltodextrin supplement.
The authors concluded, “Protein supplementation at breakfast and lunch for 24 weeks in healthy older adults resulted in a positive (1.3 pound) difference in lean muscle mass compared with an isoenergetic, nonnitrogenous maltodextrin control. These observations suggest that an optimized and balanced distribution of meal protein intakes could be beneficial in the preservation of lean tissue mass in the elderly.”
I would add two things:
- This study did not show that these protein levels were optimal. It only showed that using a protein supplement to increase protein intake at breakfast and lunch was beneficial for seniors consuming most of their protein at dinner.
- This study also did not show that a total intake of 106 grams of protein in the supplemented group was necessary for maintaining lean muscle mass.
If the 83 grams of protein in the control group were evenly divided between breakfast, lunch, and dinner it would have come to almost 28 grams of protein per meal. That would fall within the 25-30 grams of protein per meal that most experts feel is sufficient to help seniors prevent age-related loss of lean muscle mass.
Study #2: The effect of the three protein supplements at breakfast and lunch on protein intake was as follows:
| Protein Intake In Grams |
| Protein Source |
Control Phase |
Supplemental Phase |
| Collagen |
70 |
112 |
| Whey Protein |
68 |
108 |
| Pea Protein |
64 |
104 |
[Note: The amount of additional protein from the control diet plus supplementation averaged around 40 grams/meal instead of 50 grams in the supplemental protein provided. This means that study participants were actually consuming an extra 20 grams of protein at breakfast and lunch.]
Again, the results were clear cut:
- Adding ~20 grams of either whey or pea protein to a relatively low-protein (15 grams) breakfast increased muscle protein synthesis by ~9%.
- Adding ~20 grams of collagen to the same low-protein breakfast had no effect on muscle protein synthesis.
The authors concluded, “We discovered that the RDA [for protein] was insufficient to support higher rates of MPS [muscle protein synthesis] in older adults. Manipulating dietary protein to increase daily consumption of higher quality – whey and pea but not collagen – proteins by targeting the lowest protein-containing meals offers a viable strategy to enhance…MPS in older adults.”
“Consuming protein much closer to expert group consensus recommendations [1.2 gm/kg instead of the current 0.8 gm/kg for adults over 50] may help to increase…MPS with advancing age and extend health-span – compressing the years of disease and disability commonly experienced by older individuals closer to the end of life.”
My comments are:
- You may recall from the previous discussion that age-related muscle loss occurs because muscle protein synthesis (MPS) becomes less efficient as we age.
-
- Therefore, an increase in muscle protein synthesis following each meal will lead to an increase in muscle mass over time, such as was seen in the first study.
- In our 60’s and beyond we require higher amounts of both protein and leucine to maximize muscle protein synthesis.
- The collagen supplement used in this study provided enough supplemental protein. But it probably was ineffective because it only provided 0.86 grams of leucine.
-
- The amount of leucine in the control diet was not specified, but with only 15 grams of protein for breakfast there was probably enough leucine to make up for the lack of leucine in the collagen supplement.
- In contrast the whey and pea supplements provided 2.7 and 2.1 grams of leucine, respectively. When added to the leucine in the control diet, this would be more than enough to drive muscle protein synthesis.
-
- Not every pea protein supplement may be as effective as the one used in this study. When I looked it up, it was described as an “enriched pea protein designed as a soy and milk alternative.” The manufacturer did not say how it was “enriched”, but I suspect it was enriched by adding extra leucine.
- Finally, this study does not show that seniors need to consume more than 100 grams of protein per day. It simply shows that adding an extra 20 grams of supplemental protein to a low-protein meal can help maximize muscle protein synthesis and minimize age-related muscle loss.
What Do These Studies Mean For You?
 Don’t Leave Out Resistant Exercise. These studies were focused on the timing and quality of protein. But don’t forget that adequate protein and leucine are only two of the requirements for preventing age-related muscle loss. The third, and arguably the most important, is resistance exercise.
Don’t Leave Out Resistant Exercise. These studies were focused on the timing and quality of protein. But don’t forget that adequate protein and leucine are only two of the requirements for preventing age-related muscle loss. The third, and arguably the most important, is resistance exercise.
Aim for at least three 30-minute resistance exercise sessions per week. If you have physical limitations consult with your health professional about the type, duration, and intensity of resistance exercise that is right for you.
Forget What You Have Been Told About Protein. You have been told that American consume too much protein. That’s probably true for the average couch potato. But it is not true for seniors. The average American does consume too much of the wrong kind of protein, but that’s another story for another day.
You have been told that the average woman only needs 46 grams of protein per day and the average man needs only 56 grams of protein per day. That’s based on the RDA of 0.8 gm/kg (0.36 gm/pound) and an average weight of 127 pounds for women and 155 pounds for men.
We haven’t weighed that since the 50’s. Today the average woman weighs 170 pounds, and the average man weighs 201 pounds. That means protein intake should be at least 61 gm/day for women and 72 gm/day for men.
But that’s only if you are in your twenties or thirties. The consensus among those who study protein needs in seniors is that the RDA should be 1.2 gm/kg (0.54 gm/pound) for adults over 50. That’s 91 gram/day and 108 grams/day, respectively, for average weight women and men.
With that perspective, it is easy to understand the recommendation that seniors get 25-30 grams of protein and 2.5-2.7 grams of leucine per meal. That’s 75-90 grams of protein and 7.5-8.1 grams of leucine per day. But that is probably not what you are hearing from your doctor.
 Why Is Supplemental Protein Important? It’s easy to say that seniors should get 25-30 grams of protein per meal, but that’s not the way most seniors eat.
Why Is Supplemental Protein Important? It’s easy to say that seniors should get 25-30 grams of protein per meal, but that’s not the way most seniors eat.
When I was a child growing up in Alabama the standard breakfast was eggs, ham, grits with ham gravy and biscuits. I’m not saying that was a healthy breakfast, but it was the standard breakfast where I lived at the time. And it provided plenty of protein.
In today’s world most seniors have been told to avoid eggs and red meat. Breakfasts are more likely to be some type of cereal with a fruit garnish and perhaps some toast. That’s a much healthier breakfast, but it’s a low-protein breakfast. That’s why most seniors only get 8-15 grams of protein at breakfast time.
I won’t go into lunches, but similar transformations have taken place at lunch time.
So, if you want to avoid age-related muscle loss you have two choices:
- Completely change your diet and incorporate more healthy protein foods into your breakfast and lunch menus or…
- Add a protein supplement to your low-protein meals. The second study suggests that 20 grams of supplemental protein will be sufficient to transform a low-protein meal into one that will support muscle protein synthesis and minimize age-related muscle loss.
Why Is Protein Quality Important? The second study shows that having enough protein is not sufficient to stimulate muscle protein synthesis. It must be high quality protein.
The authors of the study suggested that collagen did not stimulate muscle protein synthesis due to its low leucine content.
And, as I mentioned earlier, the pea protein used in the study was “enriched” so it could be used as a “whey or soy alternate”, and the “enrichment” probably included adding extra leucine.
So, if you are planning to use a plant protein supplement with your low-protein meal(s), I would recommend choosing one with added leucine.
How Much Protein Is Too Much? The ability of a protein meal and/or supplement to stimulate muscle protein synthesis begins to plateau at around 30 grams of protein, so there is little advantage to protein intakes above 30 grams at one time. And as I said above, excess protein is stored as fat.
What About An After-Workout Supplement? Previous studies have shown that the numbers are about the same for after-workout supplements.
- For someone in their 30s, 15-25 grams of protein with 1.7 grams of leucine per meal is enough to maximize muscle gain after a workout.
- But someone in their 60s or 70s needs 25-30 grams of protein and 2.5-2.7 grams of leucine per meal to maximize muscle gain.
- After-workout supplements can also be designed to optimize the insulin response, but that is another story for another day.
One Final Pearl
 At the very beginning of this article, I told you that the breakdown of muscle protein to keep blood sugar levels constant during fasting and starvation was driven by a hormone called glucagon.
At the very beginning of this article, I told you that the breakdown of muscle protein to keep blood sugar levels constant during fasting and starvation was driven by a hormone called glucagon.
And the active ingredient in the latest weight loss drugs like Wegovy, Ozempic, and Trulicity is GLP-1, which stands for glucagon-like peptide-1.
So, it should be no surprise that those drugs cause loss of muscle mass. That’s a side effect you probably haven’t been told about.
The Bottom Line
It’s all downhill after age 50! That’s when we start to experience age-related muscle loss, something called sarcopenia.
Age-related muscle loss can be prevented with resistance exercise, adequate protein, and adequate leucine. And the amount of both protein and leucine we need to prevent muscle loss increases as we age.
Previous studies have defined the amount of protein and leucine we need to prevent muscle loss in our 60s and 70s. The studies described in today’s health tip show the benefit of adding a protein supplement to our low-protein meals and the importance of a high-quality protein supplement for minimizing age-related muscle loss.
For more information on these studies and what they mean for you, read the article above.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
_____________________________________________________________________________
My posts and “Health Tips From the Professor” articles carefully avoid claims about any brand of supplement or manufacturer of supplements. However, I am often asked by representatives of supplement companies if they can share them with their customers.
My answer is, “Yes, as long as you share only the article without any additions or alterations. In particular, you should avoid adding any mention of your company or your company’s products. If you were to do that, you could be making what the FTC and FDA consider a “misleading health claim” that could result in legal action against you and the company you represent.
For more detail about FTC regulations for health claims, see this link.
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/health-products-compliance-guidance
______________________________________________________________________
About The Author
 Dr. Chaney has a BS in Chemistry from Duke University and a PhD in Biochemistry from UCLA. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of North Carolina where he taught biochemistry and nutrition to medical and dental students for 40 years. Dr. Chaney won numerous teaching awards at UNC, including the Academy of Educators “Excellence in Teaching Lifetime Achievement Award”.
Dr. Chaney has a BS in Chemistry from Duke University and a PhD in Biochemistry from UCLA. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of North Carolina where he taught biochemistry and nutrition to medical and dental students for 40 years. Dr. Chaney won numerous teaching awards at UNC, including the Academy of Educators “Excellence in Teaching Lifetime Achievement Award”.
Dr Chaney also ran an active cancer research program at UNC and published over 100 scientific articles and reviews in peer-reviewed scientific journals. In addition, he authored two chapters on nutrition in one of the leading biochemistry text books for medical students.
Since retiring from the University of North Carolina, he has been writing a weekly health blog called “Health Tips From the Professor”. He has also written two best-selling books, “Slaying the Food Myths” and “Slaying the Supplement Myths”. And most recently he has created an online lifestyle change course, “Create Your Personal Health Zone”. For more information visit https://chaneyhealth.com.
For the past 45 years Dr. Chaney and his wife Suzanne have been helping people improve their health holistically through a combination of good diet, exercise, weight control and appropriate supplementation.
 Big Food Inc is not your friend. Big Food Inc follows the latest trends and is only too happy to give consumers what they want.
Big Food Inc is not your friend. Big Food Inc follows the latest trends and is only too happy to give consumers what they want. It’s hard to believe that breakfast cereals started as health food, but they did. Dr. John Harvey Kellogg was a Seventh-day Adventist who took over the Western Reform Health Institute in 1877 and renamed it the Battle Creek Sanitarium.
It’s hard to believe that breakfast cereals started as health food, but they did. Dr. John Harvey Kellogg was a Seventh-day Adventist who took over the Western Reform Health Institute in 1877 and renamed it the Battle Creek Sanitarium. The investigators used data from the Mintel Global New Products Database, which tracks new product launches for foods and beverages. From this database they identified 1,200 new children’s cereals introduced in the US market from 2010 through 2023.
The investigators used data from the Mintel Global New Products Database, which tracks new product launches for foods and beverages. From this database they identified 1,200 new children’s cereals introduced in the US market from 2010 through 2023.![]() If the previous decline in nutritional value of breakfast cereals between the 1870s and 1970s can be described can be described as “appalling”, the latest results can only be described as disastrous.
If the previous decline in nutritional value of breakfast cereals between the 1870s and 1970s can be described can be described as “appalling”, the latest results can only be described as disastrous.
 Dr. Chaney has a BS in Chemistry from Duke University and a PhD in Biochemistry from UCLA. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of North Carolina where he taught biochemistry and nutrition to medical and dental students for 40 years.
Dr. Chaney has a BS in Chemistry from Duke University and a PhD in Biochemistry from UCLA. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of North Carolina where he taught biochemistry and nutrition to medical and dental students for 40 years.